SpringCloud微服务搭建和调用
1 安装nacos
Nacos 致力于帮助您发现、配置和管理微服务。Nacos 提供了一组简单易用的特性集,帮助您快速实现动态服务发现、服务配置、服务元数据及流量管理。
Nacos 帮助您更敏捷和容易地构建、交付和管理微服务平台。 Nacos 是构建以“服务”为中心的现代应用架构 (例如微服务范式、云原生范式) 的服务基础设施。
首先下载nacos:https://github.com/alibaba/nacos/releases
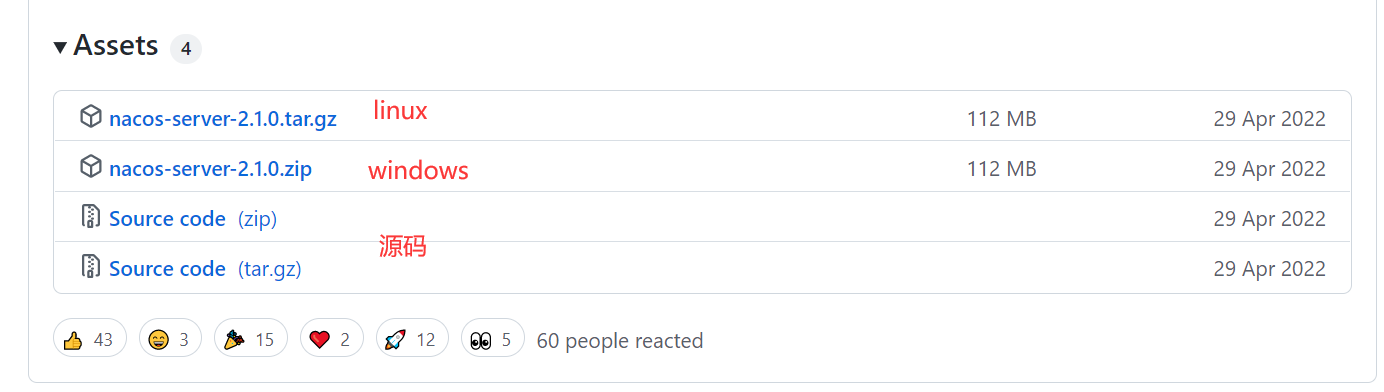
下载的时候注意:1.4.0以下使用的mysql驱动是8.0以下的,1.4.0以上使用的驱动就是8.0以上的了,所以大家在使用的nacos的时候要注意与mysql的对应版本问题,否则会因为nacos与mysql的版本不对应导致的nacos无法加载数据源。
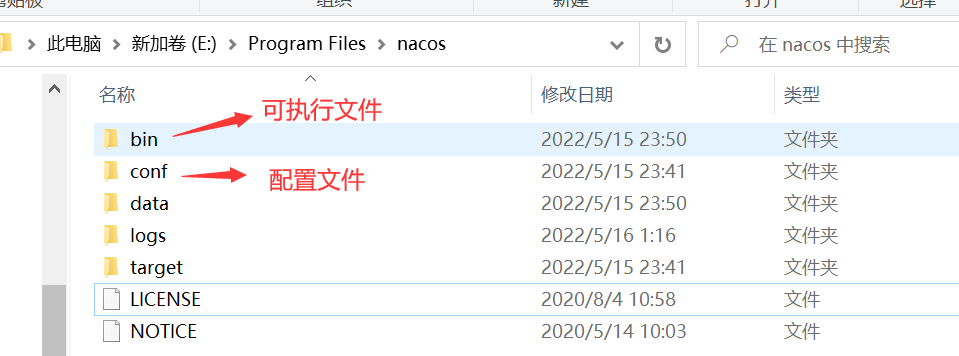
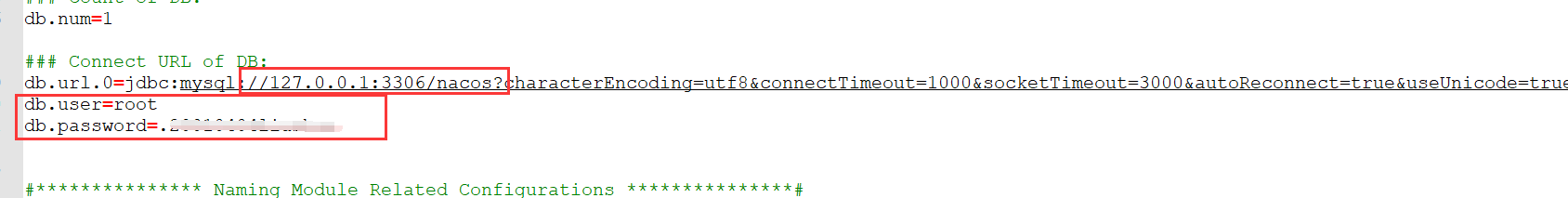
接下来需要配置数据库,进入conf目录,然后使用数据库工具建立nacos数据库,并执行下面的sql脚本
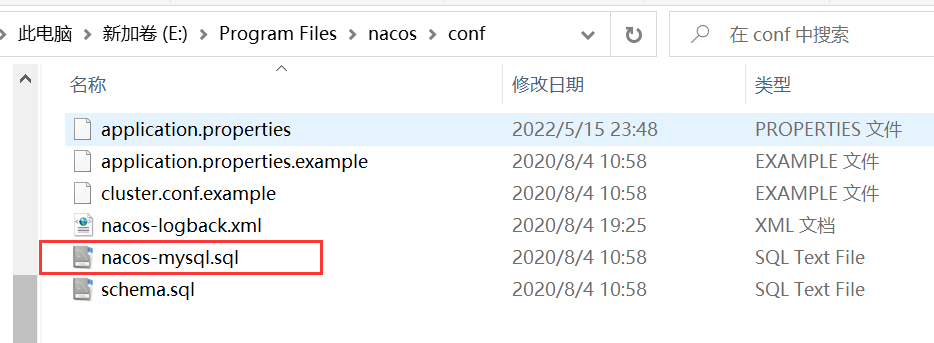
然后修改配置文件application.properties,配置数据库源,使用mysql数据源记得下面这行的注释取消掉
然后修改nacos运行模式,nacos默认使用的集群模式cluster,需要修改为单机模式standalone
Nacos支持三种部署模式,这里是用于自己测试,使用第一种就行
1、单机模式:可用于测试和单机使用,生产环境切忌使用单机模式(满足不了高可用)
2、集群模式:可用于生产环境,确保高可用
3、多集群模式:可用于多数据中心场景
修改bin目录下的startup.cmd,将启动模式设置为standalone,它默认是集群启动
之后就可以启动nacos了,启动nacos需要有java环境,如果没有配置java环境变量,需要先配置好。
双击cmd程序即可直接运行
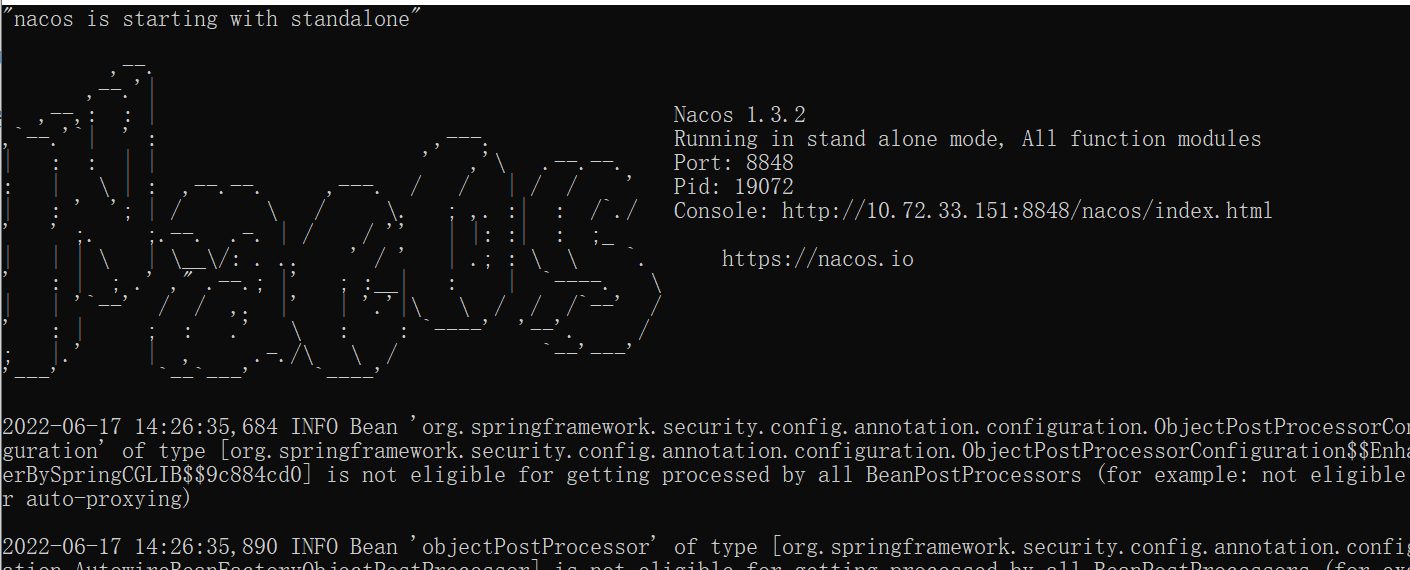
进入图中提示的Console网页,就是nacos的控制台
账号密码默认都是nacos
2 项目搭建
工程搭建
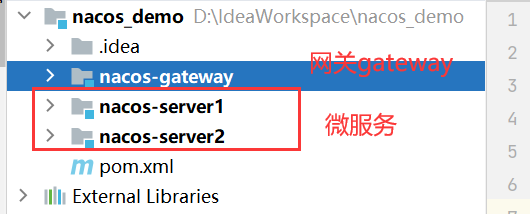
首先搭建最外层项目,这里新建一个maven项目即可。然后把所有文件都删掉,只留下一个pom.xml配置文件即可。
然后创建两个微服务,之这个maven项目下,新建module,选择springboot项目即可。这样就可以是一个父子工程,只需要在父工程里面导入一个公共的依赖,子工程就不需要额外引入了,可以直接继承。
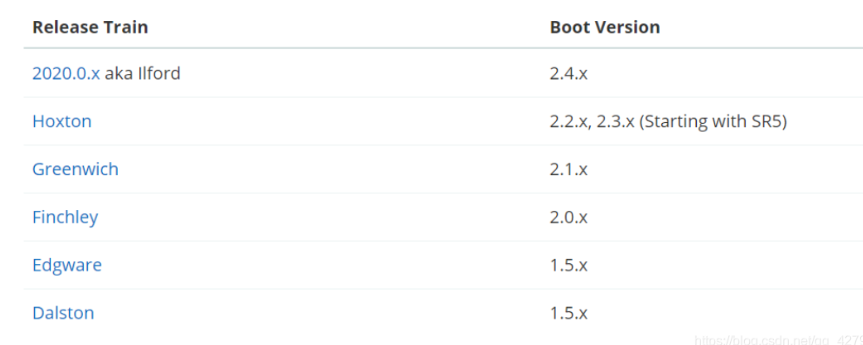
这里需要注意很大的问题,就是springboot和springcloud存在版本适配问题,需要版本对应了,才能启动成功
cloud和boot版本对照表,可以去官网
父子工程依赖配置
父工程配置pom.xml
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>nacos_demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<!-- 有了这个parent就不需要给子集pom配置版本号了,因为它包括了
1.定义了java编译版本为1.8
2.使用utf-8格式编码
3.继承spring-boot-dependencies进行统一版本依赖管理
4.执行打包 war jar操作配置(可以省略打包plugin的配置)
5.自动化资源过滤 如application.properties和application.yml的资源过滤 包括profile 多环境配置的
6.自动化插件配置
7.不需要配置maven打包plugin插件配置-->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.3.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<!--父工程配置这个文件的打包方法,不然打包的时候,这个配置文件不会打包进去-->
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<!--子项目在这注册-->
<modules>
<module>nacos-server1</module>
<module>nacos-server2</module>
<module>nacos-gateway</module>
</modules>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<!--引入springcloud的版本-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>Greenwich.SR3</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<!--国内依赖镜像仓库,可以方便下载依赖-->
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>spring</id>
<url>https://maven.aliyun.com/repository/spring</url>
<releases>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</releases>
<snapshots>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
</repositories>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
子工程pom.xml
<parent>
<!--配置引用的父工程-->
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>nacos_demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>nacos-server1</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>nacos-server1</name>
<!--子工程配置打包方式-->
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<description>nacos-server1</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--提供web服务的子项目导入这个依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--gateway子项目则导入gateway的依赖-->
<!--<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>-->
<!--其余的可以根据需要再自行引入-->
</dependencies>
springcloud配置
首先需要再每个子项目的启动类上添加@EnableDiscoveryClient注解,允许nacos服务发现

然后配置web服务的项目的application.yml文件
server:
port: 8081
spring:
application:
# 微服务的名字
name: service1
cloud:
# nacos的注册地址
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: localhost:8848
然后配置网关的application.yml文件
server:
# 统一的访问入口
port: 9999
spring:
application:
name: nacos-gateway
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: localhost:8848
gateway:
discovery:
locator:
enabled: true #开启表示根据微服务名称映射,就是微服务名称拼接到url中可以直接访问,但是不推荐这么使用 容易暴露微服务 默认false,开启后可以通过ip:port/服务名称/接口地址进行服务转发
enabled: true #默认开启网关true,关闭网关false
# 这里就是配置微服务的访问,可以实现负载均衡等功能
routes:
- id: service1 #路由的ID,没有固定规则但要求唯一,建议配合服务名
uri: http://localhost:8081 #匹配后提供服务的路由地址
predicates:
- Path=/service1/** #断言,路径相匹配的进行路由转发
- id: service2
uri: http://localhost:8082
predicates:
- Path=/service2/**
3 启动
分别启动这三个项目,即可看到这三个项目都在nacos注册了
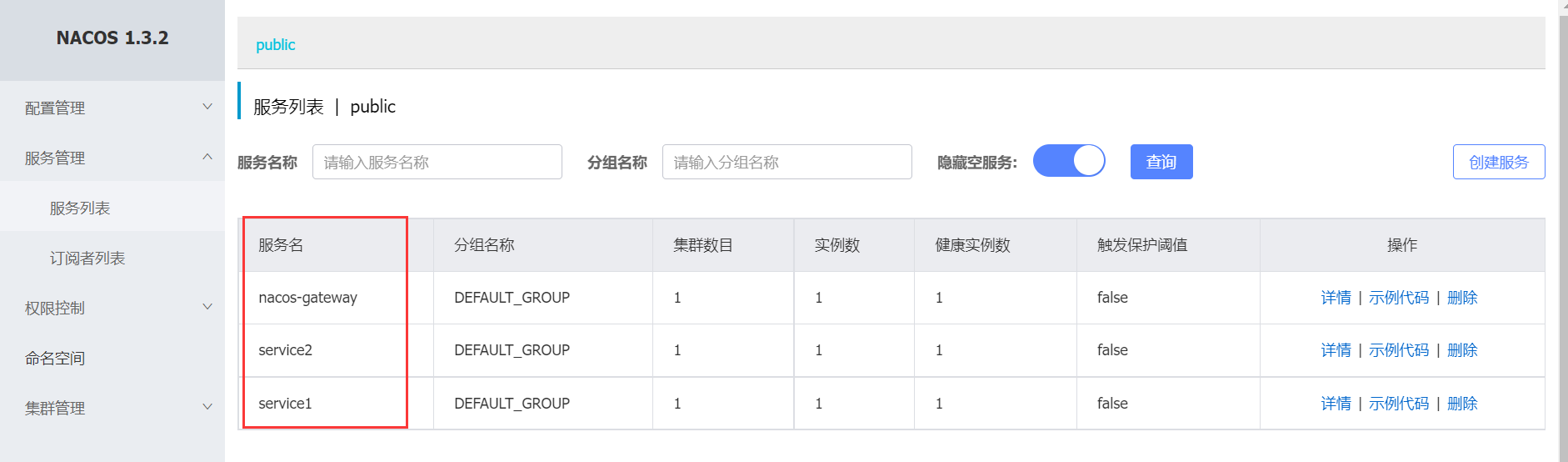
4 调用
写个简单的例子

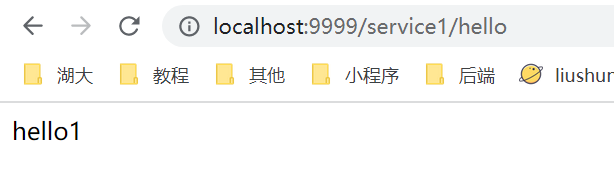
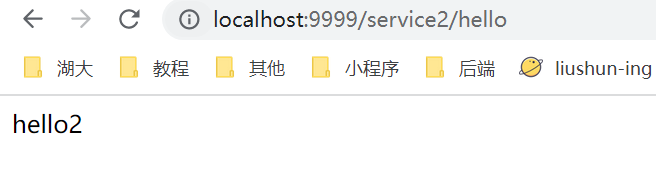
当启动了可以根据服务名匹配时,就可以使用ip:port/服务名称/接口地址进行访问
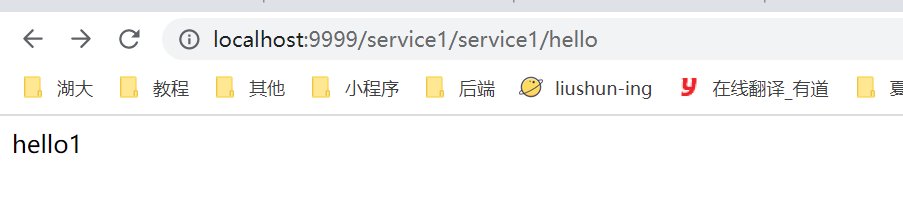
关闭之后,就不能了,只能通过自己定义的匹配规则进行访问
5 服务间调用FeignClient
feign是Springboot cloud体系下的一个重要组件,用于微服务间的调用,底层为httpClient。 feign 暂时不支持GET方式传递bean类封装的多参数对象,feign调用用GET请求传递复杂参数时,底层的urlhttpclient会自动把get方法转为post方法,因此需要针对bean类进行转换,主要有三种方式: 1)将 bean封装的多参数对象拆散成一个一个单独的属性放在方法参数里。(不适用于参数多的案例) 2)使用 GET 传递 @Requestbody(慎用),此方式违反 RESTFul 规范,要求被请求项目参数支持Requestbody,且需要将FeignClient的访问方式替换为apache下的httpclient访问方式。 3)把方法参数变成 Map 传递。 这里使用第三种方法把方法参数变成 Map 传递实现。
哪个服务用到,就操作哪个服务,一下均是操作service服务
添加依赖
<!-- feign -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
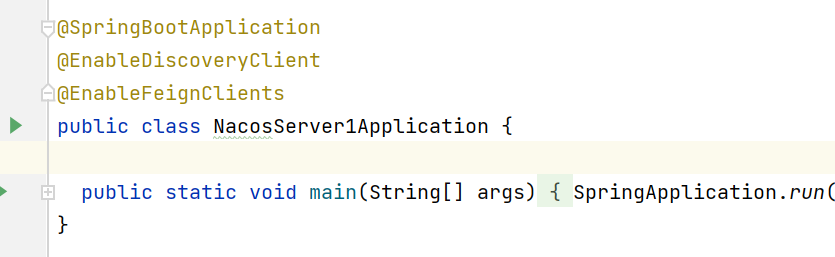
启动类添加如下注解@EnableFeignClients
然后编写代理类
package com.example.nacosserver1;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import java.util.Map;
@FeignClient(name = "service2",url = "http://localhost:8082")
@Component
public interface Server2FeignClient {
@RequestMapping("/service2/postInfo")
String postInfo(@RequestParam Map requestVo); // get请求携带对象,转换为map,加个注解就行
@RequestMapping("/service2/hello")
String hello();
@RequestMapping(value = "/service2/postInfoPost", method = RequestMethod.POST)
String postInfoPost(User user);
}
和controller类
package com.example.nacosserver1;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.CrossOrigin;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
@CrossOrigin
@RequestMapping("service1")
public class UserController {
// 自动注入接口
@Autowired
private Server2FeignClient server2FeignClient;
@RequestMapping("hello")
public String hello() {
return "hello1";
}
@RequestMapping("hello2")
public String hello2() {
// 直接调用接口的函数即可
return server2FeignClient.hello();
}
@GetMapping("postInfo")
public String postInfo(User user) {
// 使用fastjson完成对象到map的转换
return server2FeignClient.postInfo(JSON.parseObject(JSON.toJSONString(user), Map.class));
}
@PostMapping("postInfoPost")
public String postInfoPost(User user) {
return server2FeignClient.postInfoPost(user);
}
}
顺便给出service2的controller
@RequestMapping("hello")
public String hello() {
return "hello2";
}
@GetMapping("/postInfo")
public String postInfo(User user) {
System.out.println(user);
return user.toString();
}
@PostMapping("/postInfoPost")
public String postInfoPost(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println(user);
return user.toString();
}
测试:
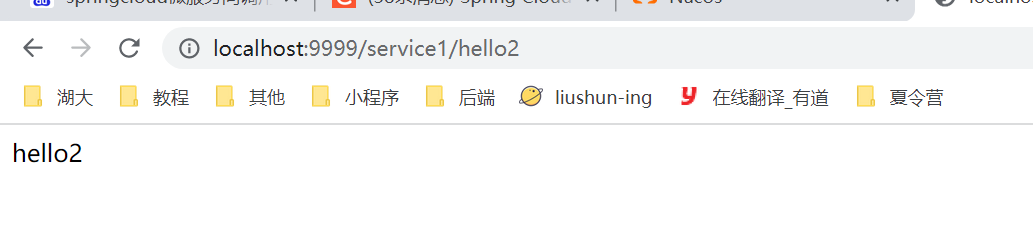
通过service调用service2的hello接口,这是无参数传递情况
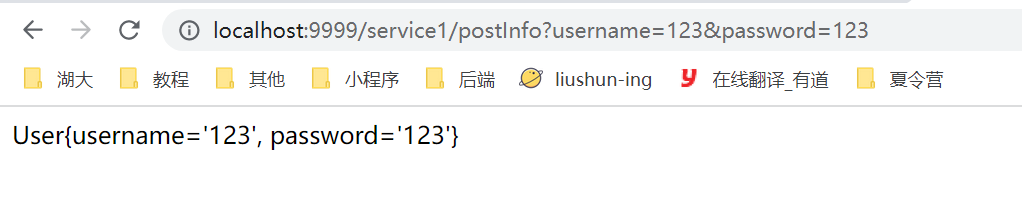
传递一个user对象,get请求,需要转换为map形式,然后feign客户端需要使用@RequestParam参数
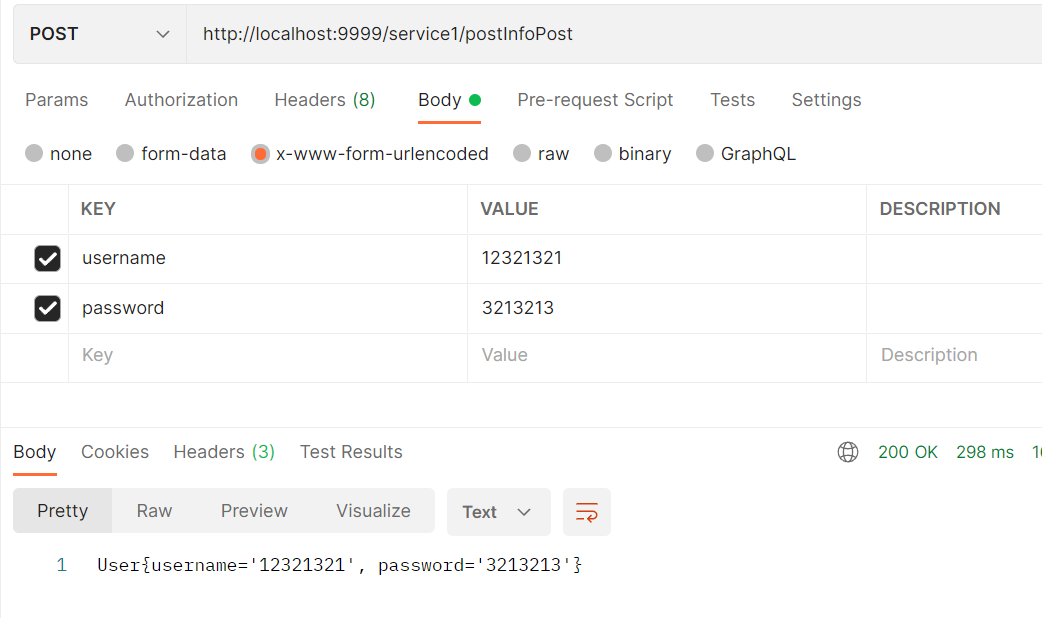
使用post请求携带请求体,可以直接使用user作为feign的参数传递,只不过需要注意的是,feign只支持json形式的请求体,所以在service2中需要使用@RequestBody注解,但是service1里面可以不用,可以使用x-www-form-urlencoded格式的请求体。
有了这些基本的框架,就可以开始学习编写微服务项目。