Redux
redux理解
学习文档
英文文档: https://redux.js.org/
中文文档: http://www.redux.org.cn/
Github: https://github.com/reactjs/redux
redux是什么
redux是一个专门用于做状态管理的JS库(不是react插件库)。
它可以用在react, angular, vue等项目中, 但基本与react配合使用。
作用: 集中式管理react应用中多个组件共享的状态。
什么情况下需要使用redux
某个组件的状态,需要让其他组件可以随时拿到(共享)。
一个组件需要改变另一个组件的状态(通信)。
总体原则:能不用就不用, 如果不用比较吃力才考虑使用。
7.1.4. redux工作流程
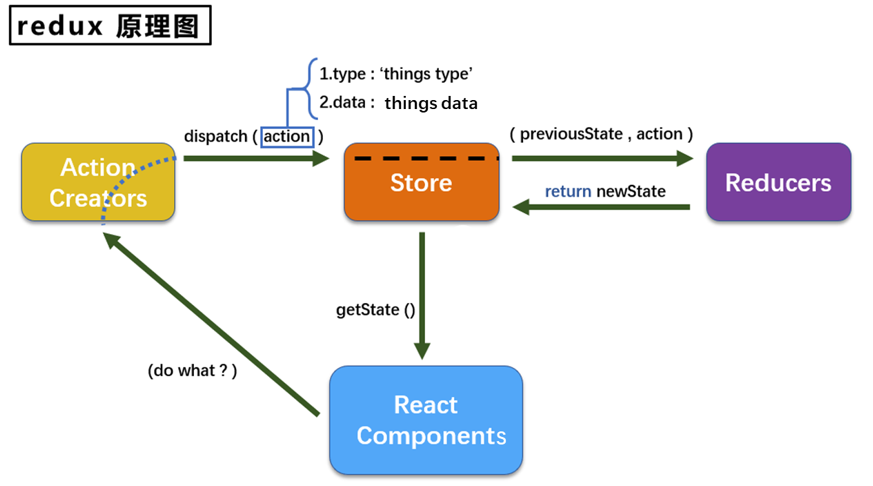
redux的三个核心概念
action
- 动作的对象
- 包含2个属性
- l type:标识属性, 值为字符串, 唯一, 必要属性
- l data:数据属性, 值类型任意, 可选属性
- 例子:{ type: 'ADD_STUDENT',data:{name: 'tom',age:18} }
reducer
- 用于初始化状态、加工状态。
- 加工时,根据旧的state和action, 产生新的state的纯函数。
store
将state、action、reducer联系在一起的对象
如何得到此对象?
- import {createStore} from 'redux'
- import reducer from './reducers'
- const store = createStore(reducer)
此对象的功能?
- getState(): 得到state
- dispatch(action): 分发action, 触发reducer调用, 产生新的state
- subscribe(listener): 注册监听, 当产生了新的state时, 自动调用
练习
简单版
(1).去除Count组件自身的状态,可以保留自己私有的state
(2).src下建立;
- -redux
- -store.js
- -count_reducer.js
(3).store.js:
- 1).引入redux中的createstore函数,创建一个store
- 2).createstore调用时要传入一个为其服务的reducer
- 3).记得暴露store对象
// 引入createStore,专门用于创建最为核心的store对象
import {createStore} from 'redux';
//引入count组件服务的reducer
import countReducer from './count_reducer'
// 暴露store
export default createStore(countReducer)
(4).count_reducer.js:
- 1).reducer的本质是一个函数,接收: preState,action,返回加工后的状态
- 2).reducer有两个作用:初始化状态,加工状态
- 3 ).reducer被第一次调用时,是store自动触发的,
- 传递的preState是undefined,
- 传递的action是:{type : ' @@REDUX/INIT_a.2.b.4}
/**
* 该文件用于创建一个reducer,本质是一个函数
* 参数为:preState前一个状态, action动作对象
*/
const initState = 0 // 初始化状态
export default function countReducer(preState=initState, action) {
const {type, data} = action
switch (type) {
case 'increment':
return preState + data
case 'decrement':
return preState - data
default:
return preState
}
}
(5).在index.js中监测store中状态的改变,一旦发生改变重新渲染
备注: redux只负责管理状态,至于状态的改变驱动着页面的展示,要靠我们自己写。
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import "./index.css";
import App from "./App";
import reportWebVitals from "./reportWebVitals";
import store from './redux/store'
ReactDOM.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<App />
</React.StrictMode>,
document.getElementById("root")
);
// 全局订阅redux,其实就是如果状态更新,就全部重新刷新页面
store.subscribe(() => {
ReactDOM.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<App />
</React.StrictMode>,
document.getElementById("root")
);
})
reportWebVitals();
使用
// 获取状态
const count = store.getState()
// 分发任务,修改状态
store.dispatch({type: 'increment', data:value*1})
完整版
新增文件:
- count_action.js 专门用于创建action对象
/**
* 专门为count组件生成action
*/
import {INCREMENT, DECREMENT} from './constant'
export const createIncrementAction = data => ({
type: INCREMENT,
data
})
export const createDecrementAction = data => ({
type: DECREMENT,
data
})
- constant.js放置容易写错的type值
/**
* 定义action对象中type类型的常量值
*/
export const INCREMENT = 'increment'
export const DECREMENT = 'decrement'
其余的地方就可以用这个代替
使用
// 获取状态
const count = store.getState()
// 改变状态
store.dispatch(createIncrementAction(value*1))
异步action版
异步和同步是说action的类型是什么,同步是对象,异步是函数
(1).明确:延迟的动作不想交给组件自身,想交给action
(2) .何时需要异步action:想要对状态进行操作,但是具体的数据靠异步任务返回(非必须)。
(3).具体编码:
npm install redux-thunk, 并配置在store中
// 引入createStore,专门用于创建最为核心的store对象
import {createStore, applyMiddleware} from 'redux';
//引入count组件服务的reducer
import countReducer from './count_reducer'
// 引入redun-thunk,用来指出异步action,并且需要applyMiddleware支持
import thunk from 'redux-thunk'
// 暴露store
export default createStore(countReducer, applyMiddleware(thunk))
- 创建action的函数不再返回一般对象, 而是一个函数, 该函数中写异步任务。
// 异步action返回值为函数,异步action中一般都会调用同步action
export const createIncrementAsyncAction = (data, time) => {
// 这个函数本身就是store调用,所以可以直接传一个dispatch参数,不需要单独引入store了
return (dispatch) => {
setTimeout(() => {
dispatch(createIncrementAction(data))
}, time);
}
}
- 异步任务有结果后,分发一个同步的action去真正操作数据。
store.dispatch(createIncrementAsyncAction(value*1, 500))
// store.dispatch({type: 'increment', data:value*1}) 可以换成上面那种写法了
备注:异步action不是必须要写的,完全可以自己等待异步任务的结果了再去分发同步action。
react-redux
理解
- 一个react插件库
- 专门用来简化react应用中使用redux
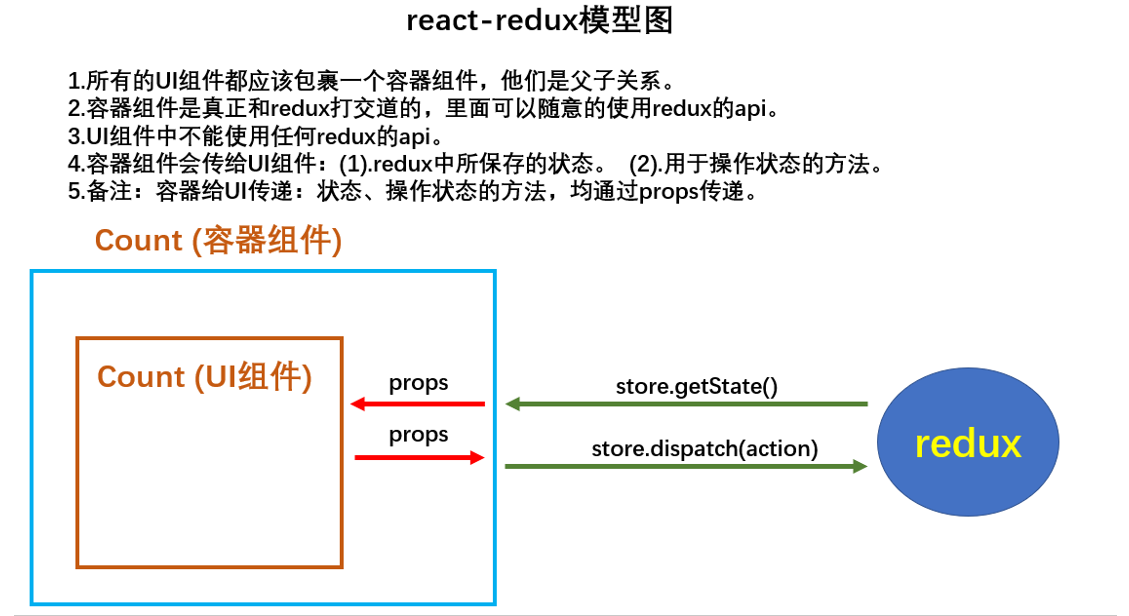
react-Redux组件分类
UI组件
- 只负责 UI 的呈现,不带有任何业务逻辑
- 通过props接收数据(一般数据和函数)
- 不使用任何 Redux 的 API
- 一般保存在components文件夹下
容器组件
- 负责管理数据和业务逻辑,不负责UI的呈现
- 使用 Redux 的 API
- 一般保存在containers文件夹下
模型图
练习react-redux版
编写
(1).明确两个概念:
- 1).UI组件:不能使用任何redux的api,只负责页面的呈现、交互等。
import React, { Component } from 'react'
export class Count extends Component {
increment = ()=>{
const {value} = this.selectNumber
// 就直接调用容器组件传过来的方法就可以
this.props.increment(value*1)
}
decrement = ()=>{
const {value} = this.selectNumber
this.props.decrement(value*1)
}
incrementIfOdd = () => {
const {value} = this.selectNumber
}
incrementAsync = () => {
const {value} = this.selectNumber
this.props.incrementAsync(value*1, 500)
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>当前求和为:{this.props.count}</ h1>
<select ref={c => this.selectNumber = c}>
<option value="1">1</option>
<option value="2">2</option>
<option value="3">3</option>
</select>
<button onClick={this.increment}>+</button>
<button onClick={this.decrement}>-</button>
<button onClick={this.incrementIfOdd}>当前求和为奇数再加</button>
<button onClick={this.incrementAsync}>异步加</button>
</div>
)
}
}
export default Count
- 2).容器组件:负责和redux通信,将结果交给UI组件。
import CountUI from "../../component/Count";
// 这个不能自己引入,需要传props
// import store from '../../redux/store'
// 引入connct用于连接UI组件和redux
import { connect } from "react-redux";
import {
createIncrementAction,
createDecrementAction,
createIncrementAsyncAction,
} from "../../redux/count_action";
/*
1.mapStateToProps函数返回的是一个对象;
2.返回的对象中的key就作为传递给UI组件props的key,value就作为传递给UI组件props的value
3.mapStateToProps用于传递状态
*/
function mapStateToProps(state) {
return { count: state };
}
/*
1.mapDispatchToProps函数返回的是一个对象;
2.返回的对象中的key就作为传递UI组件props的key, value就作为传递给UI组件props的value
3.mapDispatchToProps用于传递操作状态的方法
*/
// function mapDispatchToProps(dispatch) {
// return {
// increment: (number) => dispatch(createIncrementAction(number)),
// decrement: (number) => dispatch(createDecrementAction(number)),
// incrementAsync: (number, time) =>
// dispatch(createIncrementAsyncAction(number, time)),
// };
// }
// 简写形式,第二个参数mapDispatchToProps可以是一个对象
const mapDispatchToProps = {
increment: createIncrementAction,
decrement: createDecrementAction,
incrementAsync: createIncrementAsyncAction,
}
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(CountUI);
(2).如何创建一个容器组件--靠react-redux 的connect函数
- -connect(mapstateToProps,mapDispatchToProps)(UI组件)
- -mapstateToProps:映射状态,返回值是一个对象
- -mapDispatchToProps:l映射操作状态的方法,返回值是一个对象
(3).备注:容器组件中的store是靠props传进去的,而不是在容器组件中直接引入
import Count from './containers/Count';
import store from './redux/store';
// app.js中就只需要引入容器组件,并且传入store即可
render() {
return (
<div>
<Count store={store}></Count>
</div>
)
}
(4).备注2: mapDispatchToProps,也可以是一个对象
优化
==用了react-redux之后,index.js就不需要监听状态改变了,它会自动检测==
此外,也不需要为每一个容器组件分别添加,store属性,直接用Provider包裹App组件,就能自动进行传递
ReactDOM.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>
</React.StrictMode>,
document.getElementById("root")
);
下一个优化,
将UI组件和容器组件进行文件合并,因为最终暴露的是容器组件,UI组件只是给容器组件使用,所以可以在容器组件中直接定义UI组件,没必要单独定义了
最终只需要一个container组件
// 引入connect用于连接UI组件和redux
import { connect } from "react-redux";
import {
createIncrementAction,
createDecrementAction,
createIncrementAsyncAction,
} from "../../redux/count_action";
import React, { Component } from 'react'
class Count extends Component {
increment = ()=>{
const {value} = this.selectNumber
this.props.increment(value*1)
}
decrement = ()=>{
const {value} = this.selectNumber
this.props.decrement(value*1)
}
incrementIfOdd = () => {
const {value} = this.selectNumber
}
incrementAsync = () => {
const {value} = this.selectNumber
this.props.incrementAsync(value*1, 500)
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>当前求和为:{this.props.count}</ h1>
<select ref={c => this.selectNumber = c}>
<option value="1">1</option>
<option value="2">2</option>
<option value="3">3</option>
</select>
<button onClick={this.increment}>+</button>
<button onClick={this.decrement}>-</button>
<button onClick={this.incrementIfOdd}>当前求和为奇数再加</button>
<button onClick={this.incrementAsync}>异步加</button>
</div>
)
}
}
// 可以优化为箭头函数
function mapStateToProps(state) {
return { count: state };
}
// 简写形式,可以是一个对象
const mapDispatchToProps = {
increment: createIncrementAction,
decrement: createDecrementAction,
incrementAsync: createIncrementAsyncAction,
}
// 可以优化为直接将函数和对象填入,不需要定义一个变凉了
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(Count);
多个组件共享数据
项目结构优化:
- 每个组件一个文件夹,将容器和UI组件写在一个index.jsx文件里面
- redux中将所有的actions和reducers分别放在一个文件夹中,并且以组件名命名
- constant和store则共用
- 此外,reducers一般建一个index.js,统一将所有的reducers引入,然后conbine之后,暴露一个最终的对象,方便管理和store引入
==重点==: 每个组件的Reducer要使用combineReducers进行合并,合并后的总状态是一个对象
交给store的是总reducer,并且connect连接UI组件和容器组件时,用到的state是总state,所以需要注意取state时,注意对象取值。
组件的定义互不影响,只是需要在store.js中进行合并
//引入为Count组件服务的reducer
import countReducer from './reducers/count'
//引入为Count组件服务的reducer
import personReducer from './reducers/person'
//引入redux-thunk,用于支持异步action
import thunk from 'redux - thunk '
//汇总所有的reducer变为一个总的reducer
const allReducer = combineReducers({
count: countReducer,
allPerson: personReducer
// 这里的属性名就是组件的state想要保存的数据的名称
})
//暴露store
export default createStore(allReducer, applyMiddleware(thunk))
纯函数和高级函数
纯函数
- 一类特别的函数: 只要是同样的输入(实参),必定得到同样的输出(返回)
- 必须遵守以下一些约束
- 不得改写参数数据
- 不会产生任何副作用,例如网络请求,输入和输出设备
- 不能调用Date.now()或者Math.random()等不纯的方法
- ==redux的reducer函数必须是一个纯函数==
所以对于preState的修改,不能使用数组的push、unshift等函数,使用解构赋值构建一个新的数组代替,这样会改变传过来的参数,导致状态改变了,但是页面不会刷新(这是因为react-redux是采用的浅比较,引用没变,所以相当于state没更新)
preState.push(data) //错误
[...preState, data] // 正确
高阶函数
- 理解: 一类特别的函数
- 情况1: 参数是函数
- 情况2: 返回是函数
- 常见的高阶函数:
- 定时器设置函数
- 数组的forEach()/map()/filter()/reduce()/find()/bind()
- promise
- react-redux中的connect函数
- 作用: 能实现更加动态, 更加可扩展的功能