Netty
介绍
Netty是一个异步事件驱动的网络应用程序框架,用于快速开发可维护的高性能协议服务器和客户端。
为什么用Netty?
NIO的缺点
- NIO的类库和API繁杂,学习成本高,需要熟练掌握Selector、ServerSocketChannel、SocketChannel、ByteBuffer等。
- 需要熟悉Java多线程编程。这是因为NIO编程涉及到Reactor模式
- 臭名昭著的epoll bug。它会导致Selector空轮询,最终导致CPU 100%。直到JDK1.7版本依然没得到根本性的解决。
相对地,Netty的优点有很多:
- API使用简单,学习成本低。
- 功能强大,内置了多种解码编码器,支持多种协议。
- 性能高,对比其他主流的NIO框架,Netty的性能最优。
- 社区活跃,发现BUG会及时修复,迭代版本周期短,不断加入新的功能。
- Dubbo、Elasticsearch都采用了Netty,质量得到验证。
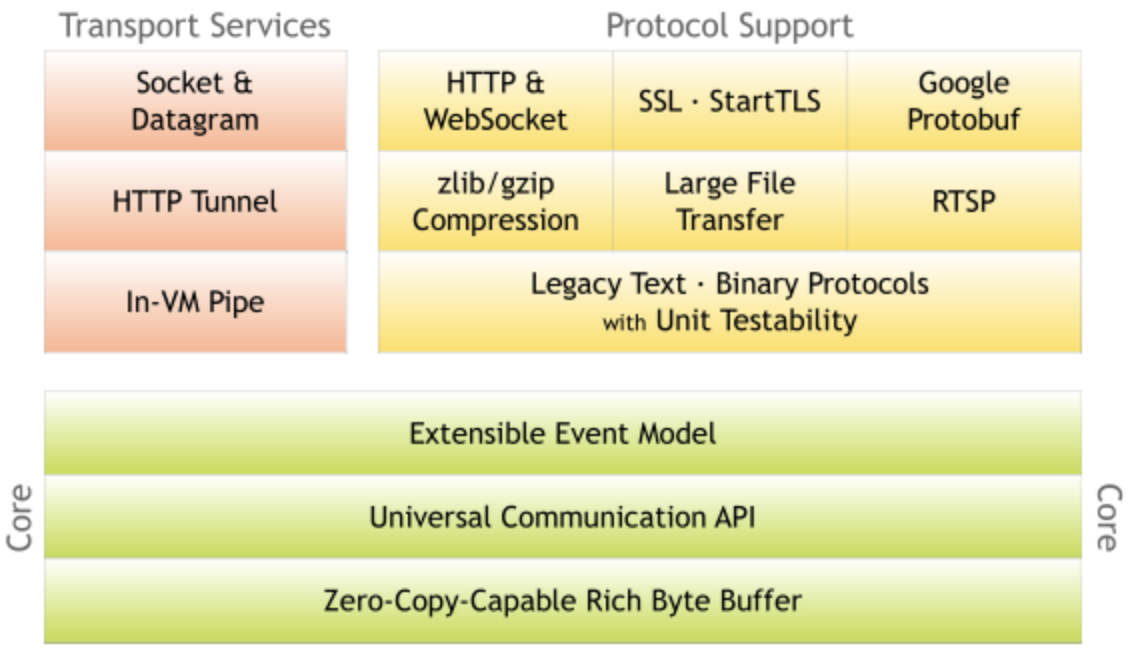
架构如图,暂时还不懂,以后有时间再看吧
Hello World
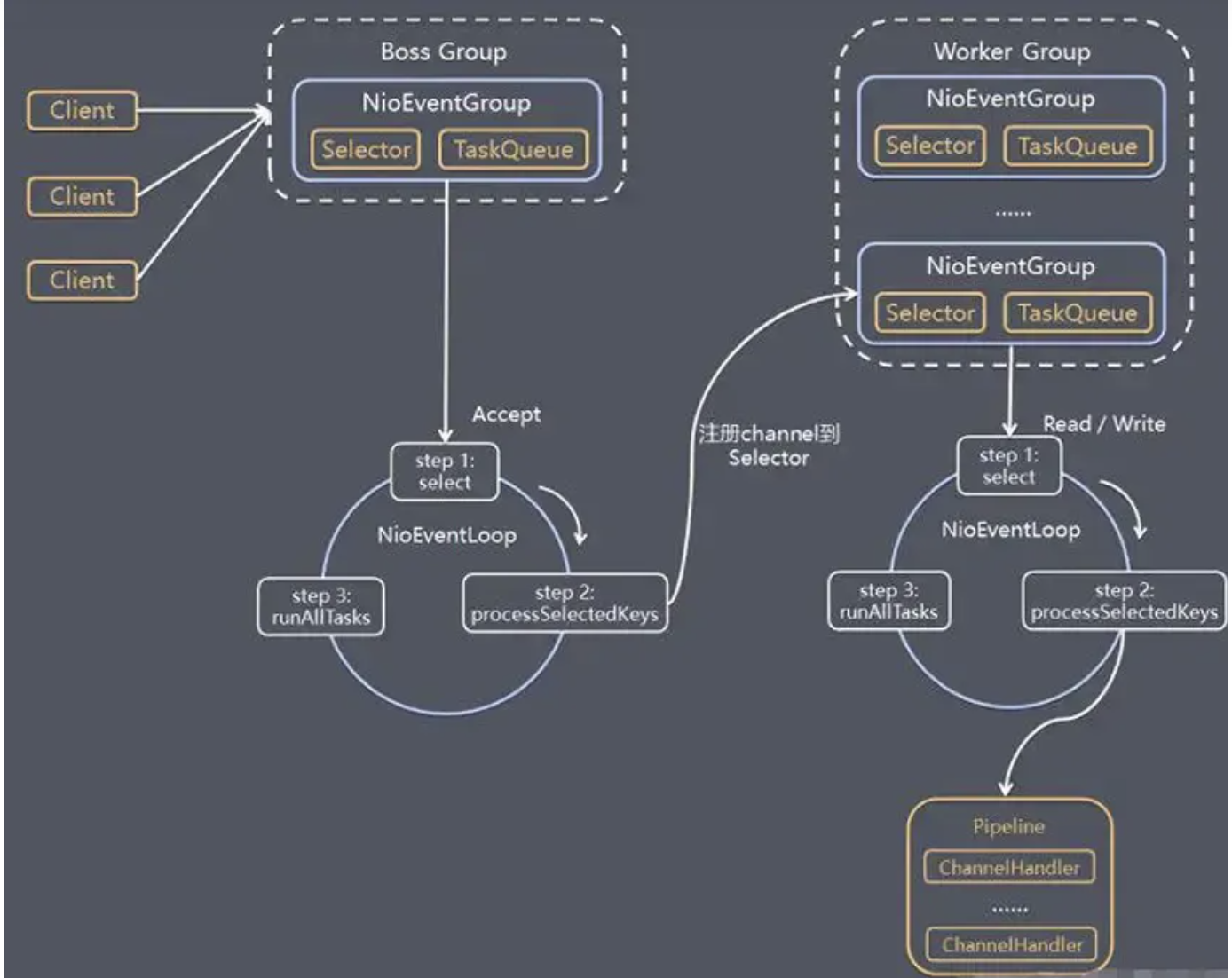
执行流程图:
- bossGroup 用于监听客户端连接,专门负责与客户端创建连接,并把连接注册到workerGroup的Selector中。
- workerGroup用于处理每一个连接发生的读写事件。
- 每个EventLoopGroup里包括一个或多个EventLoop,每个EventLoop中维护一个Selector实例。(图中NioEventGroup应该为NioEventLoop)
服务端启动类
public class MyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建两个线程组 boosGroup、workerGroup
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
//创建服务端的启动对象,设置参数
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
//设置两个线程组boosGroup和workerGroup
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
//设置服务端通道实现类型
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
//设置线程队列得到连接个数
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)
//设置保持活动连接状态
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)
//使用匿名内部类的形式初始化通道对象
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
//给pipeline管道设置处理器
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new MyServerHandler());
}
});//给workerGroup的EventLoop对应的管道设置处理器
System.out.println("服务端已经准备就绪...");
//绑定端口号,启动服务端
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.bind(6666).sync();
//对关闭通道进行监听
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
服务端处理器
/**
* 自定义的Handler需要继承Netty规定好的HandlerAdapter
* 才能被Netty框架所关联,有点类似SpringMVC的适配器模式
**/
public class MyServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
//获取客户端发送过来的消息
ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println("收到客户端" + ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + "发送的消息:" + byteBuf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
//发送消息给客户端
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("服务端已收到消息,并给你发送一个问号?", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
//发生异常,关闭通道
ctx.close();
}
}
客户端启动类
public class MyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
NioEventLoopGroup eventExecutors = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
//创建bootstrap对象,配置参数
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
//设置线程组
bootstrap.group(eventExecutors)
//设置客户端的通道实现类型
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
//使用匿名内部类初始化通道
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
//添加客户端通道的处理器
ch.pipeline().addLast(new MyClientHandler());
}
});
System.out.println("客户端准备就绪,随时可以起飞~");
//连接服务端
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 6666).sync();
//对通道关闭进行监听
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
//关闭线程组
eventExecutors.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
客户端处理器
public class MyClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
//发送消息到服务端
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("歪比巴卜~茉莉~Are you good~马来西亚~", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
//接收服务端发送过来的消息
ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println("收到服务端" + ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + "的消息:" + byteBuf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
}